Understanding Recurrent Pneumothorax Treatment: A Comprehensive Guide
Pneumothorax refers to the presence of air in the pleural cavity, which can lead to lung collapse. When this condition occurs repeatedly, it becomes known as recurrent pneumothorax. This article will delve deeply into the treatment options available for this condition, shedding light on symptoms, diagnosis, and innovative treatment strategies.
What is Recurrent Pneumothorax?
Recurrent pneumothorax is defined as the occurrence of a pneumothorax more than once in an individual. Typically, it affects young, tall males, though it can occur in anyone. It is essential to understand the underlying causes, which can be due to:
- Spontaneous Pneumothorax: Often occurs without an obvious cause, commonly in young, healthy individuals.
- Secondary Pneumothorax: May result from underlying lung conditions like chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) or cystic fibrosis.
- Traumatic Pneumothorax: Results from a direct injury to the chest.
Symptoms of Recurrent Pneumothorax
Understanding the symptoms of recurrent pneumothorax is vital for timely treatment. Common symptoms include:
- Sudden sharp chest pain: Often worsens with breathing or coughing.
- Shortness of breath: May range from mild to severe.
- Hypoxia: In severe cases, a lack of oxygen can lead to cyanosis (bluish coloration of the skin).
- Tachycardia: Increased heart rate can be a response to hypoxia or pain.
Diagnosis of Recurrent Pneumothorax
Diagnosis typically involves a combination of physical examinations and imaging studies. Key diagnostic techniques include:
- Physical Examination: Doctors may notice decreased breath sounds on the affected side.
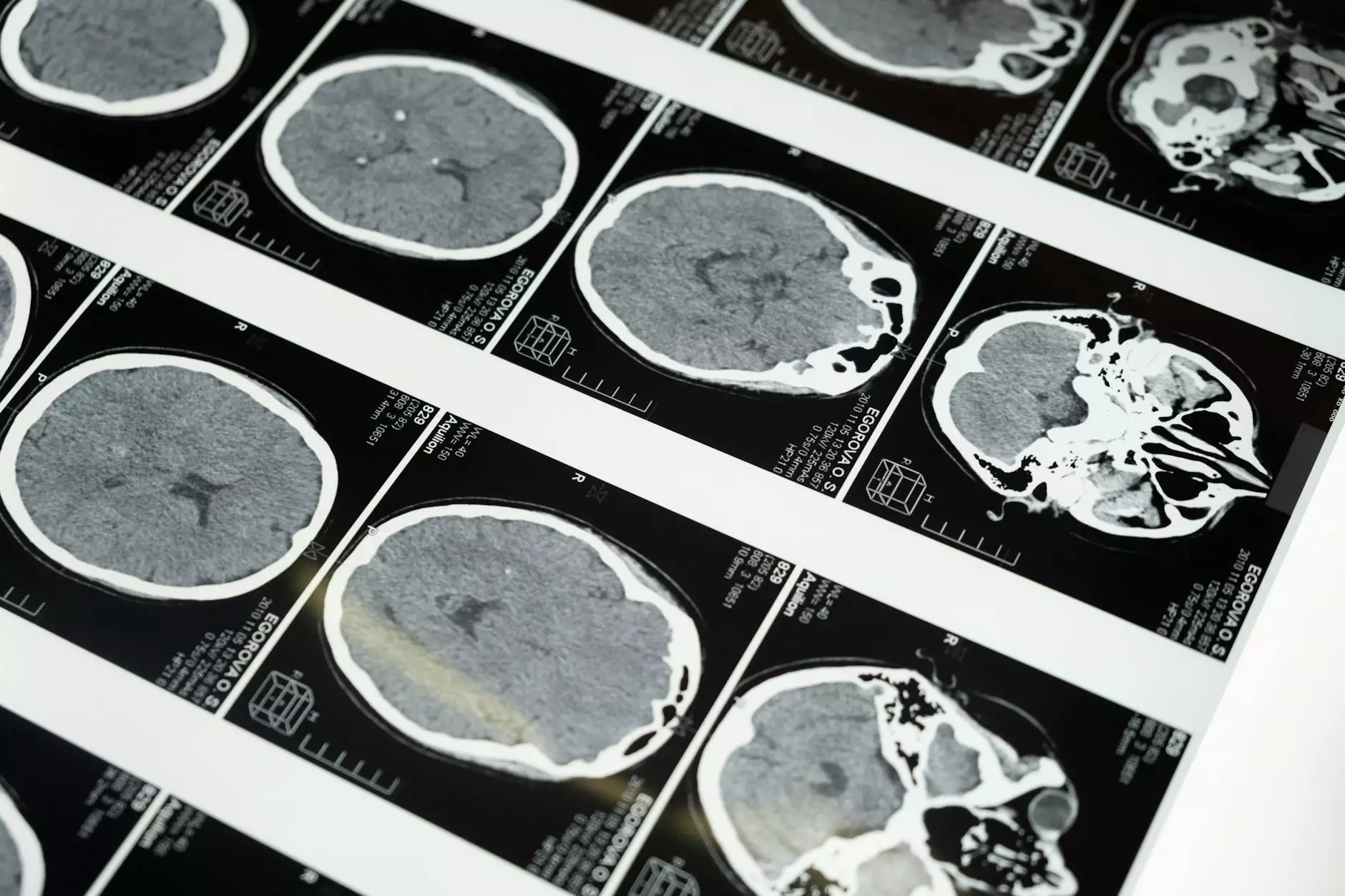
- Chest X-ray: The most common initial imaging study to confirm air in the pleural space.
- CT Scan: Provides a more detailed view of the lungs and can identify any underlying causes.
Treatment Options for Recurrent Pneumothorax
Treatment for recurrent pneumothorax can be conservative or invasive depending on the severity and frequency of occurrences.
Conservative Treatment
In cases of small, uncomplicated pneumothorax, the following methods may be employed:
- Observation: If the pneumothorax is small and not causing significant symptoms, doctors may recommend close observation with follow-up imaging.
- Oxygen Therapy: Supplemental oxygen can help speed up the reabsorption of air in the pleural space.
- Rest: Avoiding strenuous activities can prevent further complications.
Invasive Treatments
When conservative measures fail or when recurrent pneumothorax occurs, more invasive procedures may be necessary:
Needle Aspiration
This involves using a needle to remove air from the pleural space. It is a relatively simple and speedy procedure performed under local anesthesia.
Chest Tube Placement
In cases where a larger volume of air is present, a chest tube may be inserted to provide continuous drainage of air and allow the lung to re-expand.
Video-Assisted Thoracoscopic Surgery (VATS)
For recurrent cases, surgical intervention might be necessary. VATS allows for minimal invasiveness and can be used to:
- Bullectomy: Removal of blebs, which are weak areas of the lung that can lead to pneumothorax.
- Pleurodesis: This process involves using chemicals to adhere the pleura (the membrane surrounding the lungs) to the chest wall, preventing future occurrences.
Post-Treatment Management
Post-treatment management is crucial for ensuring long-term recovery and preventing recurrence. Recommendations may include:
- Follow-Up Appointments: Regular check-ups with a healthcare provider to monitor lung health.
- Avoidance of Risk Factors: Individuals should try to avoid smoking and other activities that increase the risk of pneumothorax.
- Physical Rehabilitation: Engaging in a structured rehabilitation program can help improve lung function and overall fitness.
Innovative Treatments and Research
With advancements in medical research, new treatment modalities for recurrent pneumothorax are continually being explored. Some of the latest innovations include:
- Biological Sealants: Investigating the use of sealants that can promote closure of lung blebs.
- Gene Therapy: Developing gene-modifying treatments to enhance tissue strength in the pleura.
- Endobronchial Valves: These are being studied as a potential option for patients who are not suitable candidates for surgery.
Choosing the Right Specialist for Treatment
Choosing a knowledgeable and experienced thoracic surgeon is critical when addressing recurrent pneumothorax. Here are factors to consider:
- Expertise: Look for a surgeon with extensive experience in treating pneumothorax.
- Accreditation: Ensure the medical center is accredited and utilizes advanced treatment technology.
- Patient Reviews: Reading reviews from previous patients can provide insights into the quality of care.
Conclusion
Recurrent pneumothorax can be a challenging condition that significantly impacts quality of life. However, with effective treatment options and a disciplined follow-up and management plan, patients can lead healthy, active lives. If you're struggling with recurrent pneumothorax, don't hesitate to reach out to a specialist, such as those at Neumark Surgery, who are dedicated to providing the highest level of care.
Awareness and proactive treatment are key to managing this condition effectively. Understanding the symptoms, diagnosis, and various treatment options available can empower individuals to seek the care they need promptly. Always consult with a healthcare professional for personalized advice and treatment plans.
recurrent pneumothorax treatment